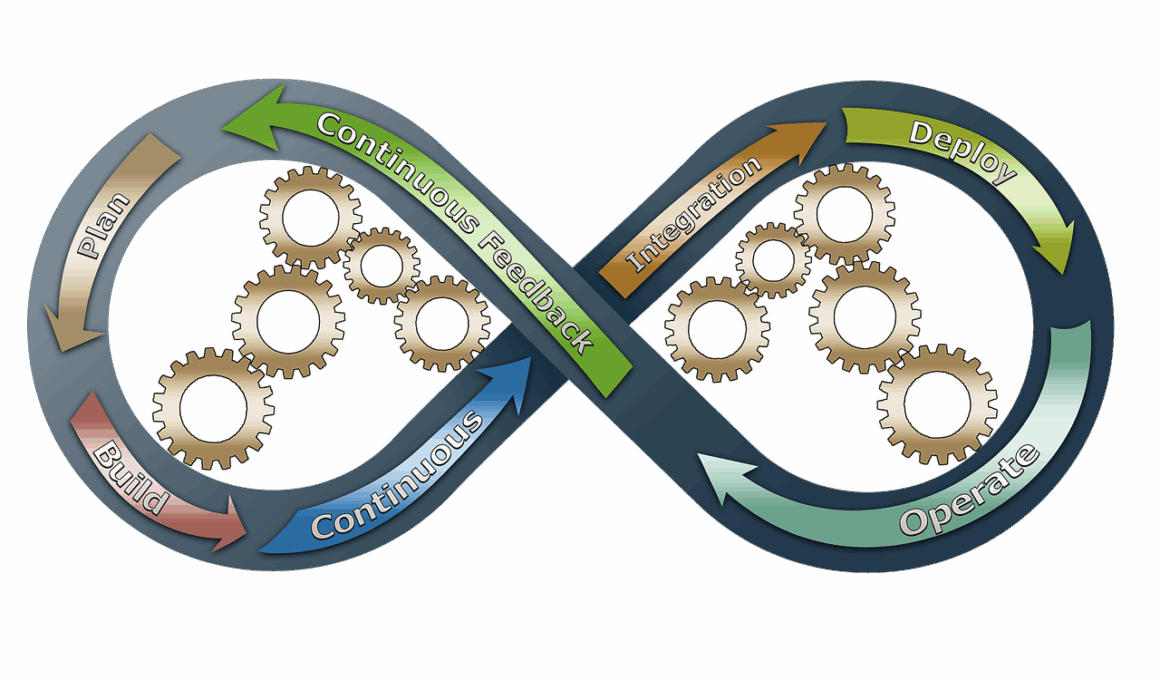
Automated Deployment using Continuous Integration in Agile Projects
Continuous Integration (CI) is a critical practice in Agile methodologies that enhances deployment efficiency. It focuses on automatically merging code changes from multiple contributors into a shared repository, thus ensuring collective development. By implementing automated testing frameworks, teams can rapidly identify and address bugs, improving software quality. As such, CI supports the Agile principle of delivering small, incremental updates. Through the use of CI tools, developers can streamline their processes, reducing integration pain and enhancing team collaboration. These tools automate the build process and integrate unit tests, allowing teams to catch issues early. Furthermore, they can be configured to deploy code to staging or production environments automatically, minimizing manual intervention. This shift to automation not only saves time but also increases reliability in deployments. Consequently, teams can iterate quickly and respond faster to customer feedback. CI alone is powerful, but when combined with practices like Continuous Delivery (CD), it significantly boosts deployment frequency and stability. In Agile projects, this combination can lead to rapid innovation and a competitive edge.
Additionally, CI promotes a culture of accountability among team members. Developers take ownership of the code they write, leading to higher quality outputs. With integrated tools, such as Jenkins, CircleCI, or Travis CI, teams can set up automated pipelines that test and deploy applications seamlessly. These tools provide instant feedback on code quality, allowing for swift adjustments. Furthermore, the integration of CI with version control systems encourages collaborative coding practices, as developers can work on new features without disrupting the main branch. Automated deployment ensures that all changes are consistently formatted and tested before reaching production, thus reducing the likelihood of deployment failures. In an Agile environment, where speed and adaptability are vital, having CI in place enables teams to maintain focus on end-user satisfaction through rapid deliveries. CI’s role extends beyond mere automation by fostering a robust and dynamic feedback loop. Developers can quickly learn from past mistakes, which enhances their ability to deliver effective solutions. By doing so, they not only improve their skills but also contribute positively to the project’s overall success.
Benefits of Automated Deployment in Agile
Automated deployment in Agile projects offers numerous benefits, making it a crucial component of CI practices. First and foremost, it significantly accelerates release cycles, allowing teams to deploy several times a day instead of weeks. This frequency is valuable as it enables businesses to respond promptly to market demands and customer feedback. Additionally, automated deployment reduces human error, ensuring that standard procedures are consistently followed without the risk of oversight. By automating build processes and tests, teams save valuable time and resources, which can be redirected towards developing features that enhance the product. Moreover, automated deployment fosters consistency across environments, which minimizes the inconsistencies that may arise due to manual processes. This uniformity leads to enhanced reliability in production environments, an essential aspect of user satisfaction. Another key advantage is the increased collaboration among team members, as everyone follows the same pipeline and deployment strategies. This transparency promotes a culture of shared responsibility where developers feel accountable for their contributions. Overall, automated deployment not only enhances efficiency but also strengthens team dynamics in Agile projects.
Furthermore, adopting automated deployment allows teams to experiment and test new features more freely. Developers can quickly roll back changes if something goes wrong during the deployment, mitigating the risk associated with deploying new code. This safety net encourages innovation as teams can explore new ideas without fearing significant setbacks. Continuous feedback during deployments also ensures ongoing improvement of code quality. Agile methodologies thrive on adaptability, and with automated deployment, teams can pivot rapidly based on user insights and analytics. By closely monitoring deployments and user interactions, teams can adjust their strategies, optimize performance, and enhance user engagement. Additionally, automated deployment tools often provide detailed logs and analytics, helping teams identify patterns that can lead to process optimization. Thus, embracing CI with automated deployment not only increases technical efficiency but also promotes a deeper understanding of the product and its users. This leads to informed decision-making that aligns with customer needs, resulting in better-designed solutions. Ultimately, those embracing CI in Agile stand to gain significant competitive advantages.
Challenges in Automated Deployment
Despite the numerous benefits, automated deployment in Agile projects also presents several challenges that teams must address. Integrating automated deployments into existing workflows can be daunting due to legacy systems and varied team skill levels. Not all team members may possess the requisite knowledge of CI/CD tools, necessitating training and adaptation. This learning curve might slow down initial adoption, creating resistance within the team. Additionally, while automation minimizes manual errors, it can lead to over-reliance on tools without proper checks and balances. This can sometimes amplify issues if the automated process encounters unexpected scenarios. Regular maintenance and updates of CI/CD systems are also essential, as outdated tools can hinder efficiency and security. Another challenge arises from the need for strong collaboration among team members; without clear communication, misalignment can occur, leading to deployment conflicts. Moreover, teams must carefully manage version control to prevent conflicts that can emerge from simultaneous changes. These challenges highlight the importance of a well-defined strategy for implementing automated deployment in Agile environments.
To successfully implement automated deployment, teams must cultivate a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement. Establishing clear communication channels enables team members to voice concerns and share insights regarding deployment processes. Regular training sessions can help bridge the knowledge gap and ensure everyone is well-versed in CI/CD practices. Additionally, establishing coding standards and testing protocols is vital for maintaining high-quality outputs. By fostering a culture of accountability, teams can ensure that all developers actively participate in monitoring deployment success. Furthermore, conducting post-mortem analyses after failed deployments can provide valuable lessons that inform future strategies. Emphasizing the need for flexibility in deployment processes also allows teams to pivot quickly if they encounter issues, ensuring reliability. In Agile methodologies, where team dynamics significantly impact success, creating a supportive environment becomes essential. Recognizing and celebrating quick cycles of improvement encourages developers to innovate, further enhancing engagement with their tasks. By addressing the challenges of automated deployment proactively, Agile teams can fully realize its immense benefits.
Conclusion: Embracing CI for Success
Embracing continuous integration and automated deployment in Agile projects can drive significant success. By facilitating quicker releases, enhancing quality, and fostering team collaboration, CI lays the foundation for more effective Agile methodologies. Teams that adopt CI effectively can maintain flexibility and responsiveness to changes while ensuring high-quality software outputs. As they navigate challenges related to implementation, a concerted effort in training and collaboration will significantly mitigate potential drawbacks. It’s important for teams to continually review and refine their processes in response to user feedback and performance metrics. This willingness to adapt and improve is critical in a fast-paced development environment where Agile thrives. Overall, CI and automated deployment reinforce the Agile manifesto’s principles, emphasizing teamwork, rapid delivery, and customer satisfaction. For teams contemplating implementing these strategies, the return on investment is evident in improved deployment frequency, increased product quality, and enhanced team morale. By making a commitment to CI practices, organizations can position themselves for ongoing success in an ever-evolving technology landscape.