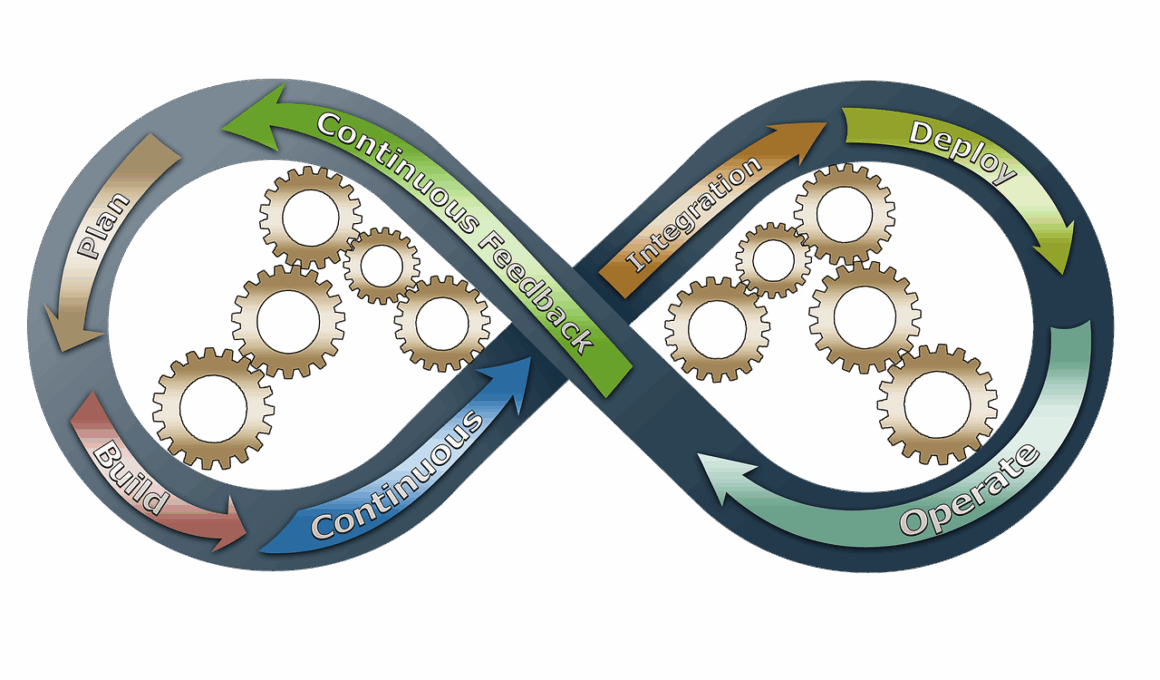
Continuous Integration (CI) in Agile DevOps
Continuous Integration (CI) serves as a foundational practice within Agile DevOps. In this process, developers frequently integrate their code into a common repository. Each integration is verified by an automated build and testing process, which helps identify problems early in the development lifecycle. By catching bugs quickly, teams can significantly enhance their workflow efficiency. CI encourages ongoing collaboration among team members, promoting shared responsibility for code quality. In addition, incorporating automated tests within CI pipelines allows teams to ensure that new code changes don’t adversely affect existing functionality. The practice also supports Agile’s iterative approach, enabling quicker delivery of features and enhancements. Furthermore, CI provides teams with immediate feedback about the status of the project. This leads to better informed decisions and allows for rapid adjustments as needed. As CI tools evolve, they increasingly integrate with other tools in the DevOps ecosystem, promoting seamless operations. In conclusion, implementing Continuous Integration is pivotal for achieving true Agile transformation, allowing teams to move faster while maintaining high-quality software. By focusing on CI, organizations can align their Agile practices with DevOps principles effectively.
Continuous Deployment (CD) builds upon the practices of Continuous Integration and is equally crucial in Agile DevOps. In CD, any code change that passes automated tests is deployed automatically to production environments. This ensures that new features and updates reach users without delays, maintaining high velocity in development cycles. Automating the deployment process reduces the chances of human error significantly, ensuring smooth transitions from development to production. As a result, organizations can deliver changes frequently, fostering a responsive and adaptive business model. Furthermore, implementing Continuous Deployment facilitates immediate user feedback, which can be used to make rapid improvements. By continuously monitoring deployed applications, teams can identify and resolve issues quickly, improving overall stability. Organizations can also maintain competitive advantages by releasing innovative features sooner than competitors. A robust CD pipeline typically includes various stages, such as building, testing, and deploying code, each handled by automated tools. Each stage is designed to ensure quality and performance, acting as a safety net for production systems. In summary, Continuous Deployment accelerates the release of software products, aligning perfectly with Agile principles while minimizing downtime.
Benefits of CI/CD in Agile Practices
The adoption of CI/CD practices in Agile environments offers numerous benefits that enhance overall project performance. First and foremost, CI/CD accelerates development cycles, allowing teams to deliver features and fixes to users at unprecedented speeds. This is particularly advantageous in today’s fast-paced market where user expectations continuously evolve. Additionally, the automation of both testing and deployment processes leads to higher levels of accuracy and efficiency. Manual errors are reduced, and the reliability of code deployments is significantly improved. Emphasizing quality through automated testing means that potential issues are caught early on, drastically reducing costs associated with fixing bugs after the product is delivered. Another important advantage of adopting CI/CD is the improved collaboration among development and operations teams. In Agile DevOps, both teams work towards a shared goal, breaking down silos and enhancing communication. This collaborative atmosphere encourages innovation and problem-solving. Furthermore, CI/CD provides vital metrics and insights regarding deployment statuses and testing outcomes, enabling data-driven decision-making for future development cycles. Ultimately, CI/CD fosters a culture of continuous improvement within Agile DevOps, leading to superior software quality.
Challenges in implementing CI/CD practices should not be overlooked, as they can impact the success of Agile DevOps. One of the primary challenges is managing the complexity of continuous integration and deployment processes. Often, organizations face difficulties in setting up automated pipelines that integrate seamlessly with existing workflows. This can lead to frustration and discourage teams from fully adopting CI/CD practices. Additionally, legacy systems may not be compatible with CI/CD methodologies, requiring considerable effort to refactor or modernize existing codebases. Resistance to change is another obstacle that can slow down implementation. Team members accustomed to traditional workflow models may be hesitant to shift towards automated approaches. Moreover, achieving a high level of test coverage is essential for the success of CI/CD, yet developing adequate test suites can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. Organizations must also invest in tools and infrastructure that support CI/CD, which can pose financial challenges, especially for smaller teams. Lastly, ensuring effective monitoring and logging mechanisms is crucial but often neglected, leading to challenges in maintaining software stability over time. Addressing these challenges early enhances the likelihood of successful CI/CD adoption.
Best Practices for CI/CD Implementation
Implementing best practices for CI/CD can significantly increase the likelihood of success within Agile DevOps environments. First, it’s essential to embrace a culture of collaboration among development, operations, and quality assurance teams. This collaborative mindset encourages shared ownership of deployments and fosters better communication channels. Second, investing in reliable CI/CD tools is critical. Organizations should select tools that align with their existing technical stack and support integrations with numerous services. Third, establishing a robust feedback loop is paramount, where development teams receive immediate insights from automated tests. This enables quick adjustments and higher-quality outcomes. Furthermore, it’s important to create a well-defined branching strategy. Following practices such as feature branching or trunk-based development ensures effective version control. In addition, regularly updating CI/CD pipelines to incorporate new features and optimizations keeps the processes agile. Finally, organizations should provide ongoing training and support for all team members to fully leverage the capabilities of CI/CD tools. By following these practices, teams are well on their way to achieving effective CI/CD implementation in Agile DevOps.
Monitoring and observability play a critical role in maintaining CI/CD pipelines, providing insights into application performance and deployment success. Continuous monitoring allows teams to identify issues quickly and address them in real time, preventing downtime and negatively impacting user experiences. Tools that provide comprehensive dashboards displaying vital statistics help teams maintain an eagle eye on software health. Additionally, observability enables teams to delve deeper into application behaviors and user interactions. By gathering detailed data on application usage, teams can make informed decisions regarding performance improvements and feature enhancements. Implementing robust logging practices contributes to effective monitoring, helping teams trace issues back to specific builds or deployments. Furthermore, creating alerts that notify teams of any irregularities or concerning trends ensures proactive management of CI/CD pipelines. Regular reviews and assessments of performance metrics lead to continual enhancements. The insights drawn from monitoring not only contribute to maintaining software stability but also enhance the Agile DevOps process itself. In summary, embracing monitoring and observability practices fortifies CI/CD initiatives, ensuring higher quality and more reliable software delivery processes.
Future Trends in CI/CD
As we look towards the future, several trends in CI/CD are poised to shape the landscape of Agile DevOps significantly. One emerging trend is the increased use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in optimizing CI/CD pipelines. These technologies can help anticipate issues, streamline processes, and improve decision-making based on historical data. Another trend is the expansion of serverless computing, which allows developers to focus on writing code without managing infrastructure. This can create faster deployment times and reduced operational overhead, aligning closely with Agile principles. Moreover, the rise of GitOps, which integrates Git version control systems into operational workflows, offers an exciting new approach to managing deployments. The integration of security within CI/CD processes, often referred to as DevSecOps, is also gaining traction, as organizations aim to shift security left in the development process. Furthermore, enhancing the cloud-native approach in CI/CD practices makes scaling applications easier. Finally, increased emphasis on compliance automation is expected to facilitate faster and more efficient adherence to regulatory requirements. These trends indicate a bright future for CI/CD methodologies in Agile DevOps.