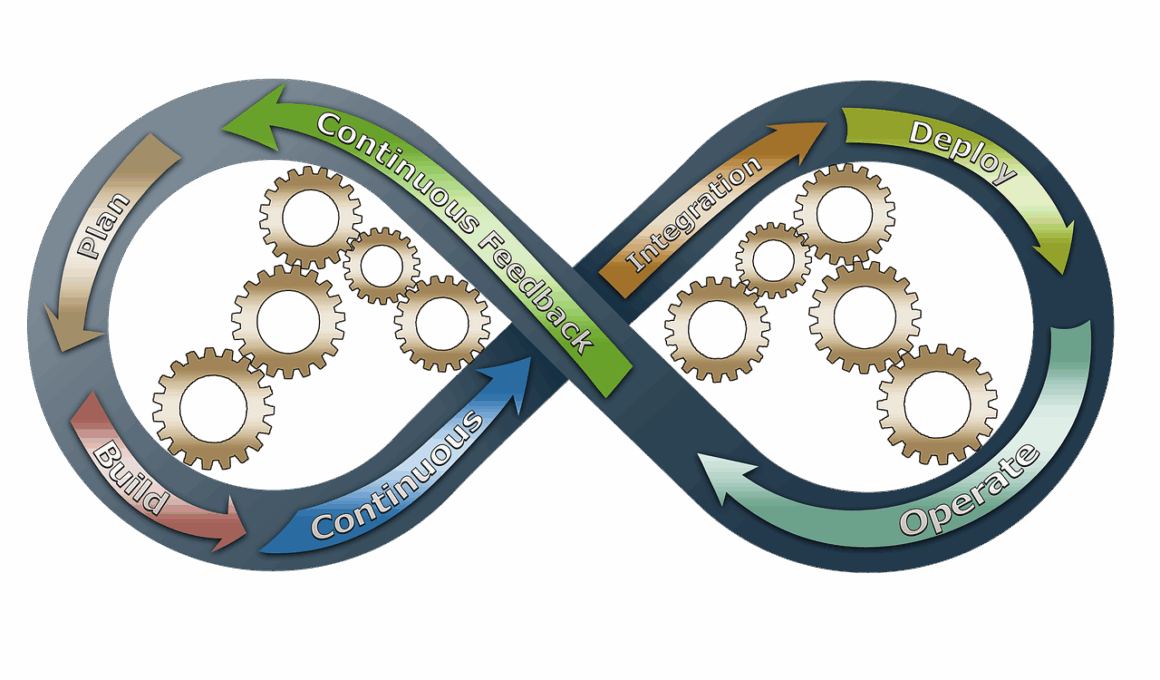
Continuous Delivery Workflows: Best Practices for Agile Teams
In today’s fast-paced software development landscape, continuous delivery (CD) has become an essential practice for Agile teams. It allows developers to deliver code changes quickly, ensuring that products remain relevant and competitive. This methodology emphasizes automation, enabling teams to deploy changes to production effortlessly. To achieve successful continuous delivery, teams must adopt best practices that streamline the release process. One of the key practices involves maintaining a well-defined branching strategy in version control systems. This ensures a clean integration of new features while minimizing disruptions. Moreover, utilizing feature flags effectively allows teams to toggle functionalities without deploying new code, granting flexibility in rollout schedules. Regularly performing automated testing is another best practice that can safeguard against defects in code. This testing should cover unit tests, integration tests, and system tests, ensuring comprehensive coverage. Furthermore, promoting a culture of collaboration among team members facilitates smoother communication, which is crucial in Agile environments. Teams should also gather and act on user feedback promptly, allowing them to respond to market needs quickly.
The importance of monitoring in continuous delivery cannot be overstated. By employing robust monitoring tools, Agile teams can gain insights into user interactions with their applications. This data is invaluable, enabling teams to identify potential issues before they escalate into significant problems. Additionally, establishing clear metrics for success can guide teams in assessing the effectiveness of their deployments. These metrics may include performance indicators, user engagement, and error rates, providing a holistic view of the product’s health. Further, implementing a rollback strategy is critical. In the event of an unsuccessful deployment, teams must quickly revert to a stable version to avoid disrupting the user experience. This ensures minimal downtime and maintains user trust. Moreover, documentation plays a pivotal role in continuous delivery workflows. Each deployment should be carefully logged, detailing what changes were made, why they were enacted, and what results were observed. This collective knowledge aids future deployments and fosters continuous improvement. Teams should also invest in training and resources to ensure everyone is well-versed in the tools and practices of continuous delivery, reinforcing their commitment to excellence.
Challenges in Implementing Continuous Delivery
Despite the numerous advantages of continuous delivery, Agile teams often face several challenges during its implementation. A primary challenge includes resistance to change from team members accustomed to traditional release processes. Transitioning to CD requires a cultural shift, encouraging teams to embrace new tools and techniques. To mitigate this inertia, leadership must actively support the change by providing the necessary resources and training. Another common hurdle is the complexity of integrating various tools and technologies. Many teams utilize multiple software for different aspects of the development cycle, leading to integration issues. Choosing tools that are compatible and can seamlessly work together is essential for smooth workflows. Security concerns also arise in continuous delivery. Rapid deployments can increase vulnerabilities if security is not prioritized. Therefore, incorporating security practices into every stage of the delivery process is crucial. This practice is often termed ‘DevSecOps,’ emphasizing that security should be integral rather than an afterthought. Lastly, managing dependencies effectively can be a challenge. Regularly updating dependencies and ensuring compatibility within the ecosystem is vital for the long-term success of continuous delivery initiatives.
To foster a successful continuous delivery approach, leveraging DevOps practices is highly beneficial. The synergy between development and operations enhances collaboration and streamlines processes. DevOps practices encourage teams to work together more seamlessly, aligning their objectives and minimizing silos. Automating infrastructure provisioning through tools like Infrastructure as Code (IaC) can lead to faster setups and consistent environments. Whether it’s deploying new services or scaling existing applications, automation mitigates errors and saves time. Additionally, implementing continuous integration (CI) alongside continuous delivery amplifies the effectiveness of CD. CI ensures that every code change is tested and merged into a shared repository frequently. This leads to immediate feedback, helping teams identify and rectify issues faster. To complement this, a thorough quality assurance process must be in place. QA teams should work in tandem with development to establish criteria for acceptance and performance. This collaboration ensures that only the highest quality code is released to production. Moreover, involving stakeholders throughout the process ensures that their requirements are met, enhancing overall project success and satisfaction amongst users and clients alike.
Automating Deployment Pipelines
Automating deployment pipelines represents a cornerstone of continuous delivery in Agile environments. This automation enables consistent, repeatable processes which significantly reduce human error during deployments. Teams can leverage tools like Jenkins, CircleCI, or GitLab CI for building and managing these pipelines effectively. These tools facilitate running tests, packaging applications, and deploying to production environments automatically. Notably, integrating automated testing at various stages within the pipeline ensures code quality is upheld. With each commit, the pipeline is triggered to run tests, providing instant feedback on potential issues. Furthermore, utilizing Docker or similar containerization technologies simplifies the management of deployment environments by enabling consistency across different stages. This consistency prevents “works on my machine” syndrome, promoting reliability in deployments. As teams develop and deploy with greater frequency, implementing robust rollback mechanisms becomes more critical. Using automation for these mechanisms allows quick reversion to previous state in case of issues. Complementarily, detailed logging within the pipeline aids in tracking the deployment lifecycle, allowing teams to monitor performance and make informed decisions about future changes. Consequently, automation ensures Agile teams can focus on innovation rather than the burdens of manual processes.
Another vital factor in enhancing continuous delivery workflows is the implementation of microservices architecture. By breaking up applications into smaller, manageable components, teams can develop, test, and deploy these services independently. This leads to increased flexibility and speed in the development process since changes to a service do not necessitate a full application deployment. Furthermore, microservices can be scaled individually based on demand, optimizing resource usage and improving application performance. However, this approach also introduces complexities, such as managing inter-service communication and data consistency. Employing proper API management strategies and service discovery mechanisms can mitigate these complexities. Additionally, ensuring that each microservice has comprehensive automated tests is essential for maintaining system reliability. Each deployment should happen without fear of breaking the entire application, emphasizing the need for robust testing frameworks. Furthermore, promoting a culture of shared ownership can enhance collaboration among team members working on different microservices, ensuring that quality and accountability are maintained. Teams can leverage agile ceremonies, such as daily stand-ups and retrospectives, to facilitate communication and collaboration effectively, resulting in a more productive development process.
Embracing a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Finally, the essence of continuous delivery lies in fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Agile teams must continually evaluate and refine their processes to maximize efficiency and quality. This approach involves regularly reflecting on past experiences to identify areas for enhancement. Agile retrospectives serve as a platform for this evaluation, allowing teams to discuss challenges and successes. Teams should encourage every member to contribute insights, fostering a shared sense of ownership and community. Prioritizing learning and development can empower teams to adopt new technologies and practices, ensuring they stay ahead in technological advancements. Moreover, setting measurable goals can drive focus, urging teams to aim for specific outcomes. Data-driven decision-making facilitates improvements based on objective analysis rather than assumptions. Alongside this, teams should not hesitate to experiment with innovative solutions and iterate on feedback. Such experimentation may lead to unexpected breakthroughs in efficiency or performance. Ultimately, by embracing this culture, Agile teams can position themselves for sustained success. They become adaptable in responding to evolving market demands while delivering exceptional products that resonate with users and stakeholders alike.
In conclusion, continuous delivery is a powerful approach that helps Agile teams to deliver high-quality software at an increased speed. By adopting best practices such as automation, embracing monitoring, and implementing robust pipelines, teams can effectively streamline their workflows. Tackling challenges proactively, leveraging DevOps principles, and fostering collaboration enhances these efforts further. The integration of microservices and a commitment to continuous improvement solidifies the foundation for ongoing evolution in development teams. As the landscape of software development continues to change, maintaining flexibility and adaptability will be crucial for Agile teams. Organizations that cultivate such environments position themselves to meet user expectations effectively while remaining competitive. Furthermore, continuous feedback loops create pathways for innovation, ensuring teams can pivot when necessary. In essence, the journey to efficient continuous delivery is not merely a series of steps; rather, it is an evolving process that requires dedication and openness to change. The benefits of implementing continuous delivery practices are profound, resulting in not only quicker releases but also enhanced product quality that delights users. By embracing these methodologies, Agile teams will set themselves up for long-term success in the ever-evolving world of software development.